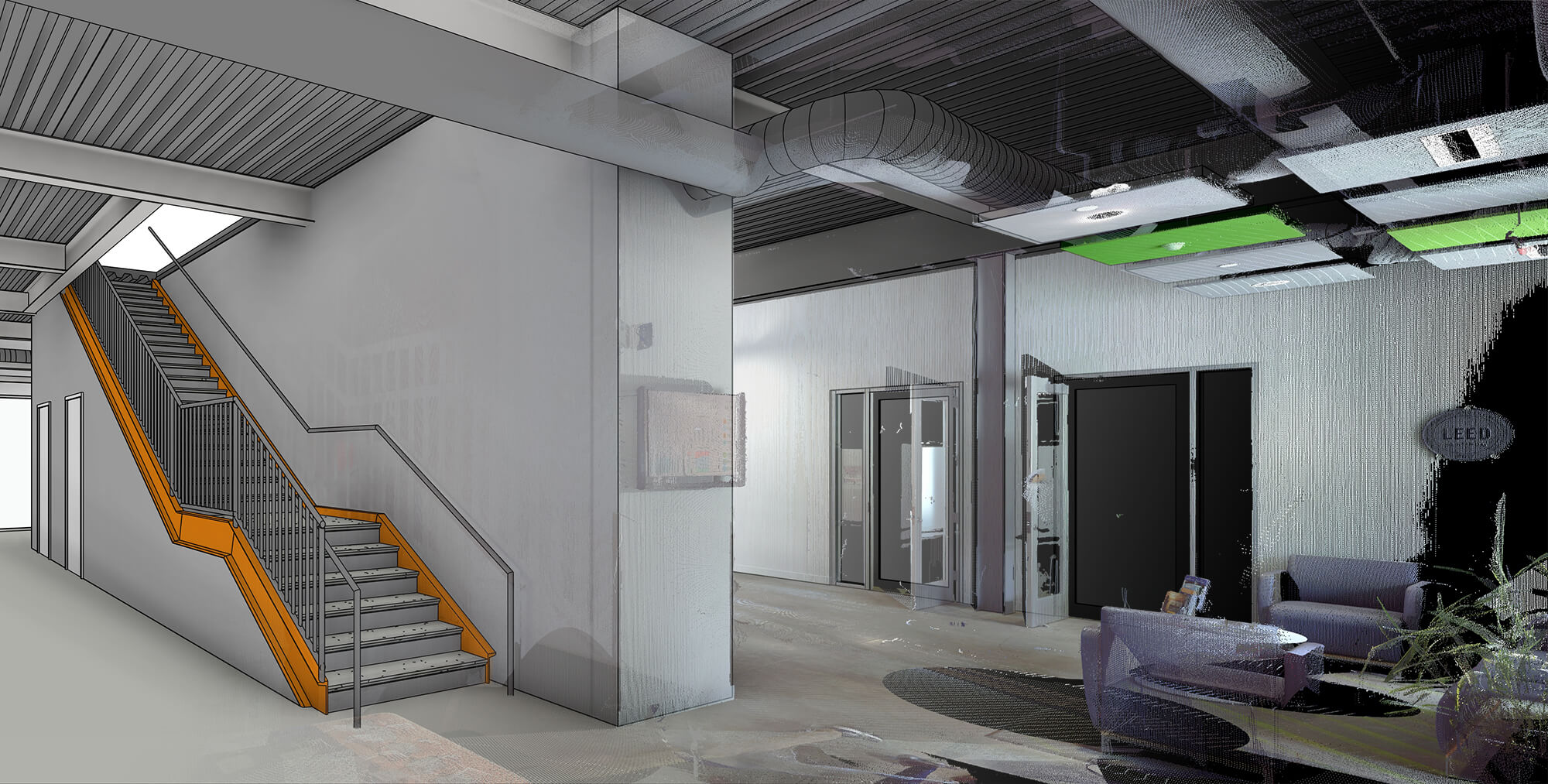
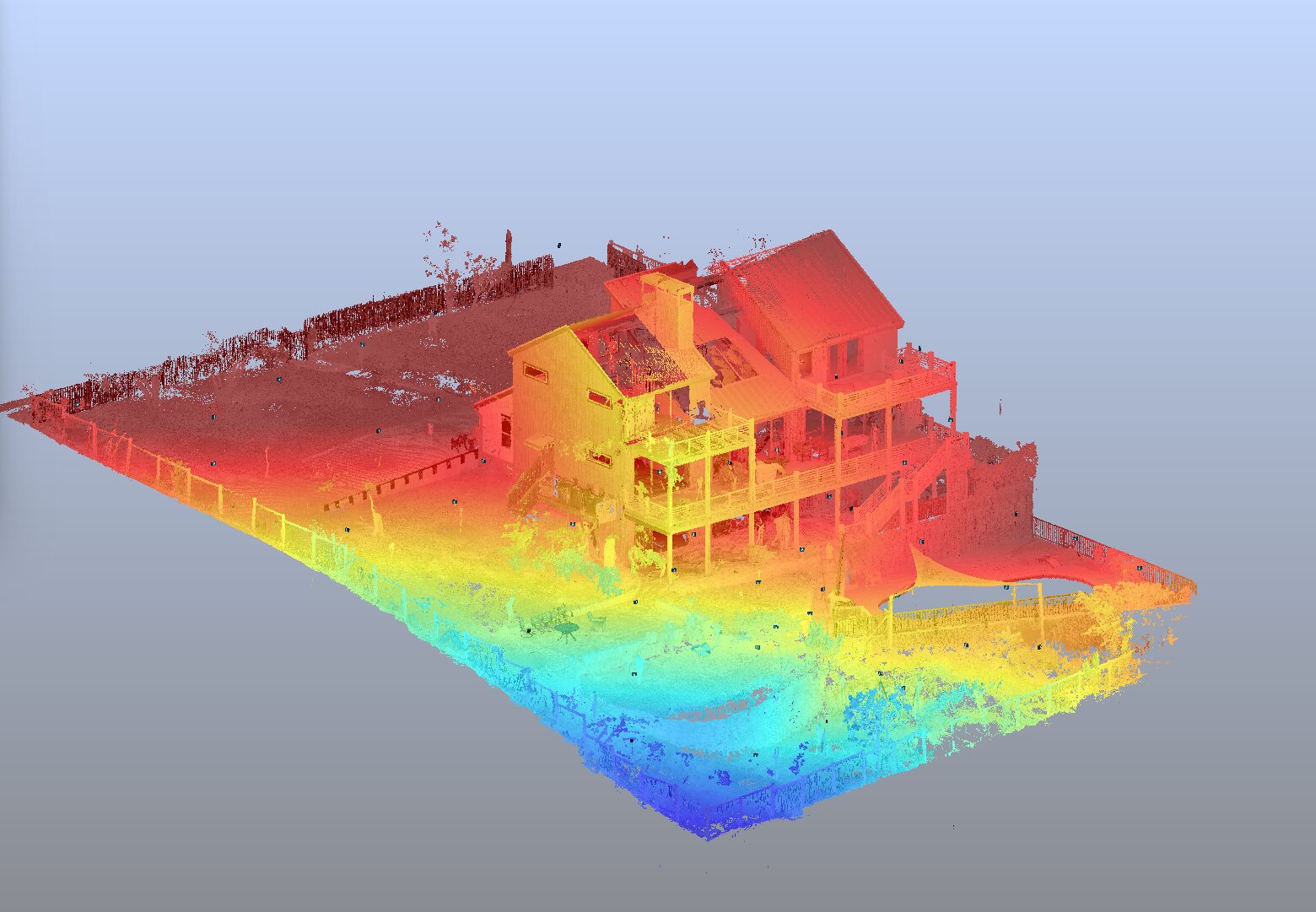
LiDAR technology has rapidly evolved over the past few decades, becoming an essential tool in civil engineering. As the technology continues to advance, it is important for civil engineers to stay informed about future trends and developments. This article explores the future of LiDAR technology, discussing market growth trends, technological advancements, and potential innovations.
Market Growth and Trends
The market for LiDAR technology is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for accurate and efficient surveying methods. According to various market research reports, the LiDAR market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10-22.2% over the next decade, reaching a market size of up to $11.83 billion by 2030. Factors contributing to this growth include advancements in LiDAR technology, increasing infrastructure development projects worldwide, and the adoption of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and digital twins.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in expanding the capabilities of LiDAR systems. Innovations in solid-state LiDAR, for example, promise smaller, more reliable, and less expensive units, making the technology more accessible for various applications. The integration of LiDAR with other sensor technologies, such as photogrammetry and UAVs (drones), is also enhancing its versatility and effectiveness. These advancements are opening up new possibilities for LiDAR applications in civil engineering, from urban planning and infrastructure monitoring to environmental conservation and disaster management.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, LiDAR technology is not without its challenges and limitations. Environmental conditions, such as heavy rain, fog, or snow, can reduce the accuracy of LiDAR data by scattering or absorbing laser pulses. Additionally, LiDAR sensors have limitations in penetrating dense vegetation, resulting in incomplete data for surfaces beneath thick forest canopies. The high cost of LiDAR equipment and the complexity of data processing are also significant barriers to widespread adoption. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these challenges and improving the reliability and affordability of LiDAR technology.
Potential Innovations
The future of LiDAR technology includes further miniaturization, cost reduction, and integration with other sensor technologies, expanding its applications in various industries. Innovations in photonics and optics are expected to lead to even more compact and efficient LiDAR systems, with applications in areas not previously imagined. For civil engineers, these innovations could mean more precise and efficient tools for surveying, monitoring, and managing infrastructure projects, ultimately contributing to safer, more sustainable built environments.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology is poised to play an increasingly important role in civil engineering as advancements continue to enhance its capabilities and affordability. LiDAR Mapping Services, particularly LiDAR Mobile Mapping Services, offer significant advantages for projects that require accurate and rapid data collection over large areas or in challenging environments. By utilizing these services, civil engineers can capture detailed spatial information that improves the accuracy, efficiency, and sustainability of their projects.
As LiDAR technology evolves, LiDAR Mapping Services are expanding to include mobile applications, which allow for more flexible data collection on moving vehicles. This innovation enables engineers to quickly gather high-resolution data, even in dynamic or difficult-to-reach areas, opening up new possibilities for innovation and development in the field of civil engineering. By staying informed about these future trends and developments, civil engineers can leverage these cutting-edge technologies to enhance their project outcomes and drive advancements in infrastructure planning and management.