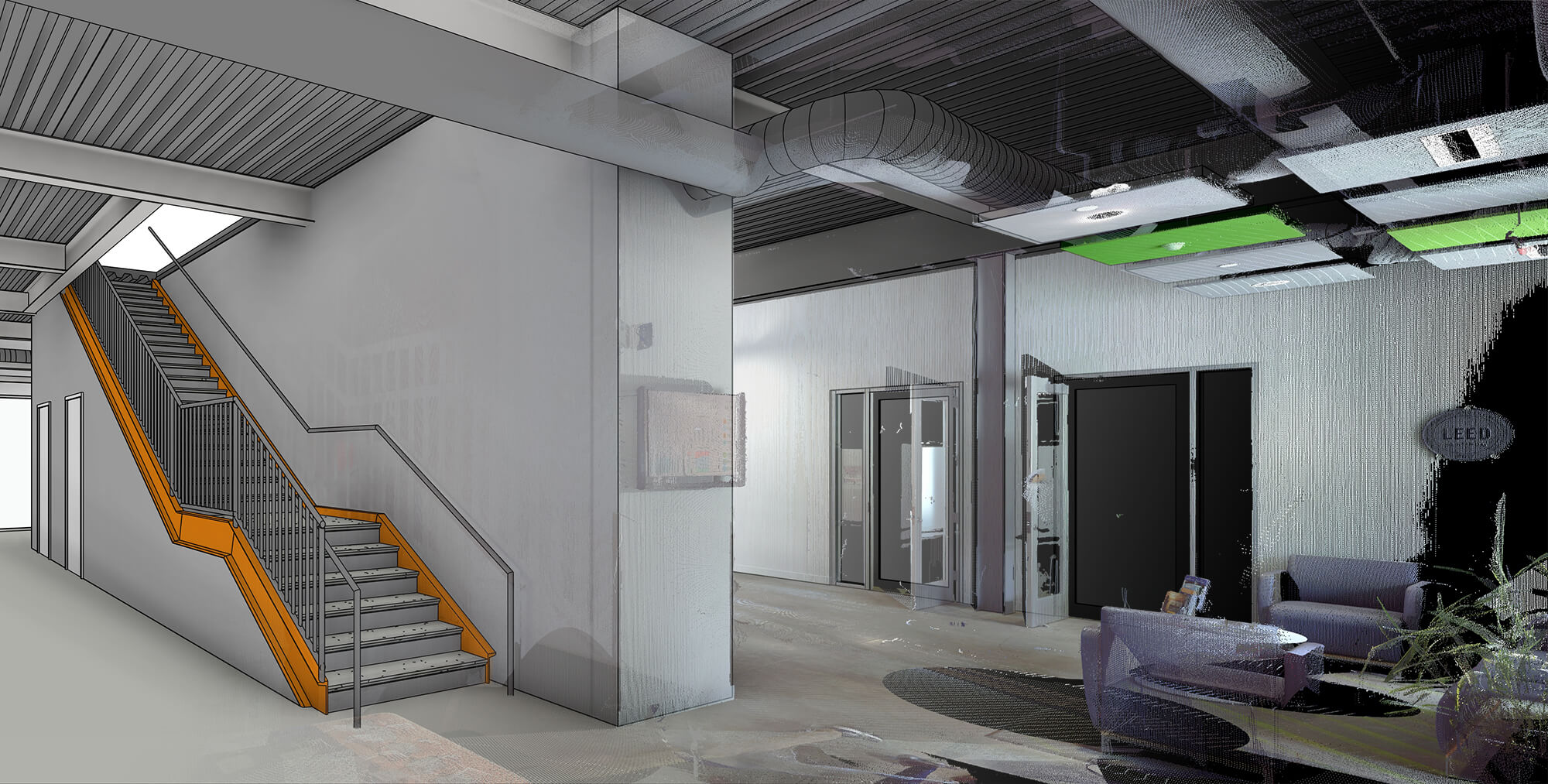
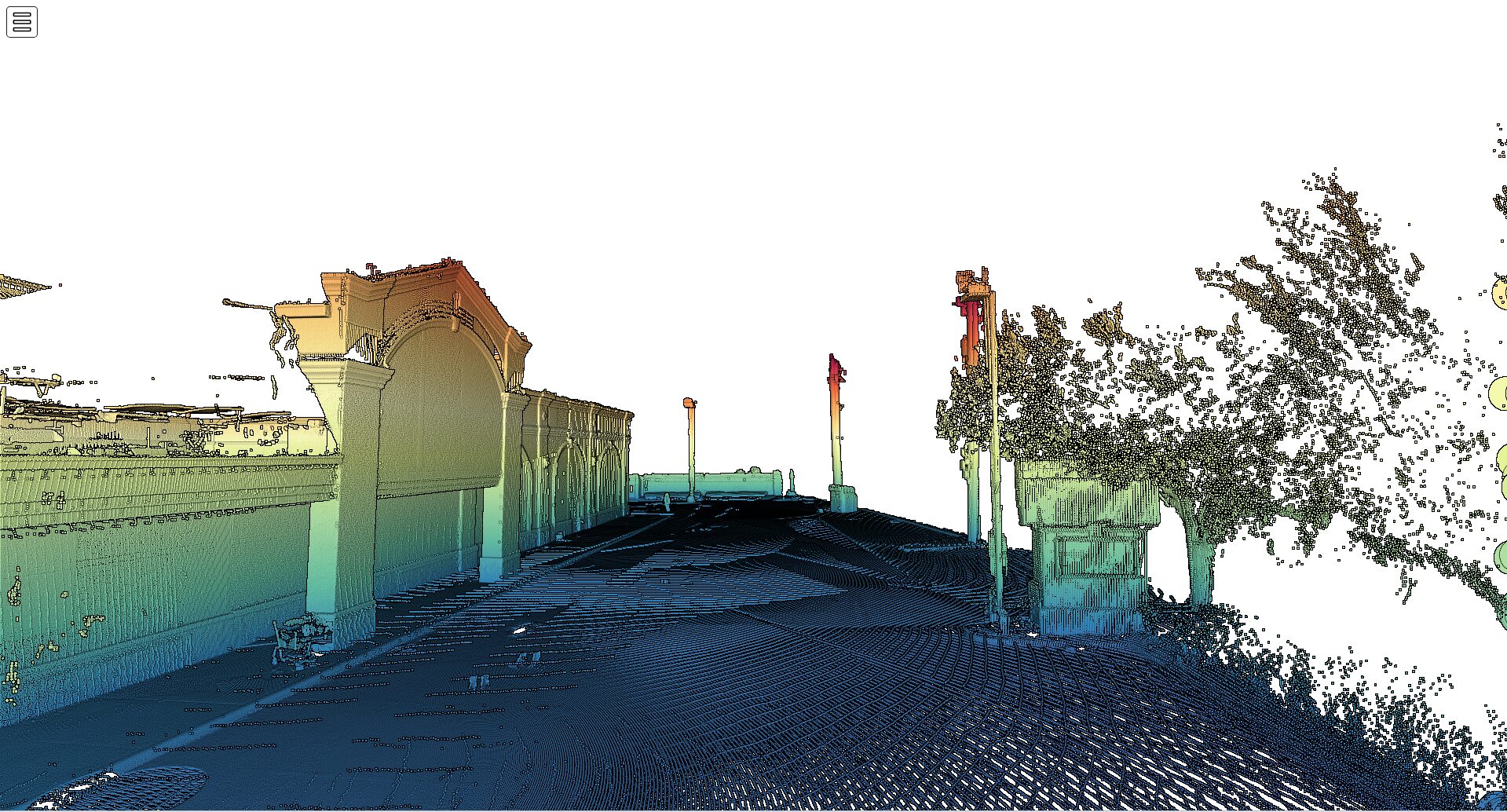
LiDAR technology has emerged as a powerful tool in civil engineering, offering a range of applications that enhance the accuracy and efficiency of infrastructure projects. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Mobile LiDAR Mapping, explaining how it works, its components, and its various applications in civil engineering.
How LiDAR Works?
LiDAR technology functions on the principle of time-of-flight. A LiDAR instrument consists of a laser, a scanner, and a specialized GPS receiver. The system emits pulses of light towards a target, and the light that reflects back to the sensor is used to calculate the distance it traveled. By measuring the time it took for the pulse to return and knowing the speed of light, the distance can be calculated with high accuracy. This process is repeated thousands of times per second to generate a dense cloud of data points, known as a point cloud, which represents the external surface of the objects that the laser pulses hit.
What are the components of LiDAR Systems?
The main components of a LiDAR system include the laser source, scanner and optics, photodetector and receiver circuit, position and orientation system (POS), data processing unit, power supply, control unit, and data storage. Each component plays a crucial role in the operation of the LiDAR system, ensuring accurate data collection and processing. For instance, the scanner directs the emitted laser beams across the survey area, while the photodetector captures the reflected light and converts it into electrical signals for distance calculation.
How many Types of LiDAR?
There are several types of LiDAR systems used in civil engineering, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Airborne LiDAR is ideal for mapping large areas quickly, while terrestrial LiDAR provides extremely detailed data for structural analysis and inspection. Mobile LiDAR Mapping, mounted on vehicles, is flexible and efficient for surveying roads, bridges, and urban areas. UAV (drone) LiDAR is useful for accessing difficult terrain without risking survey crews, and solid-state LiDAR offers a more durable and cost-effective option for various applications.
Applications in Civil Engineering
LiDAR technology is extensively applied in civil engineering for the assessment, planning, design, construction, and maintenance of critical infrastructure. It is used for accurate and detailed topographic surveys, environmental impact assessments, infrastructure monitoring, and asset management. Engineers also use LiDAR data to create precise 3D models of both natural and built environments, which are crucial for the design of infrastructure such as bridges, tunnels, and highways that integrate with the landscape.
Integration with Other Technologies
LiDAR data is often integrated with other technologies, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Building Information Modeling (BIM), to enhance the data available for the entire lifecycle of a building or infrastructure project. By combining LiDAR data with GIS, engineers can perform spatial analysis of natural and built environments. Incorporating LiDAR data into BIM processes allows for lifecycle management of buildings and infrastructure, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information is available for decision-making.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology has become an indispensable tool in civil engineering, providing fast, accurate, and high-resolution spatial data that underpins critical tasks in surveying, planning, monitoring, and managing infrastructure. By understanding how LiDAR works and its various applications, civil engineers can leverage this technology to enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and sustainability of their projects.