Understanding Rail As-Built Surveys:
Rail as-built surveys involve the systematic collection and documentation of crucial data related to railway assets, including tracks, overhead lines, signaling systems, bridges, and tunnels, among others. This survey technique employs state-of-the-art technologies, such as LiDAR, high-definition imagery, and advanced GPS tracking, to capture accurate and detailed information.
The Significance of Rail As-Built Surveys:
1. Enhancing Safety and Compliance:
By providing an accurate representation of the existing rail infrastructure, as-built surveys help identify potential safety hazards and compliance issues. This information allows engineers and maintenance teams to promptly address any shortcomings, ensuring the safety and well-being of passengers and personnel alike.
2. Efficient Planning and Maintenance:
Rail as-built surveys provide an up-to-date and granular view of the rail assets, assisting in effective long-term planning and proactive maintenance programs. With this comprehensive understanding, decision-makers can prioritize necessary repairs, replacements, or upgrades, reducing downtime and optimizing operational efficiency.
3. Streamlining Expansion and Upgrades:
For railway expansion or modification projects, rail as-built surveys play a critical role in providing accurate measurements and data. This information facilitates the seamless integration of new elements into the existing infrastructure, minimizing disruptions and reducing project timelines.
Working Methodology of Rail As-Built Surveys:
1. Initial Evaluation:
Experienced surveyors assess the rail network, identifying the scope of the survey and specific assets that require documentation. This evaluation provides a roadmap for the subsequent data collection process.
2. Data Collection:
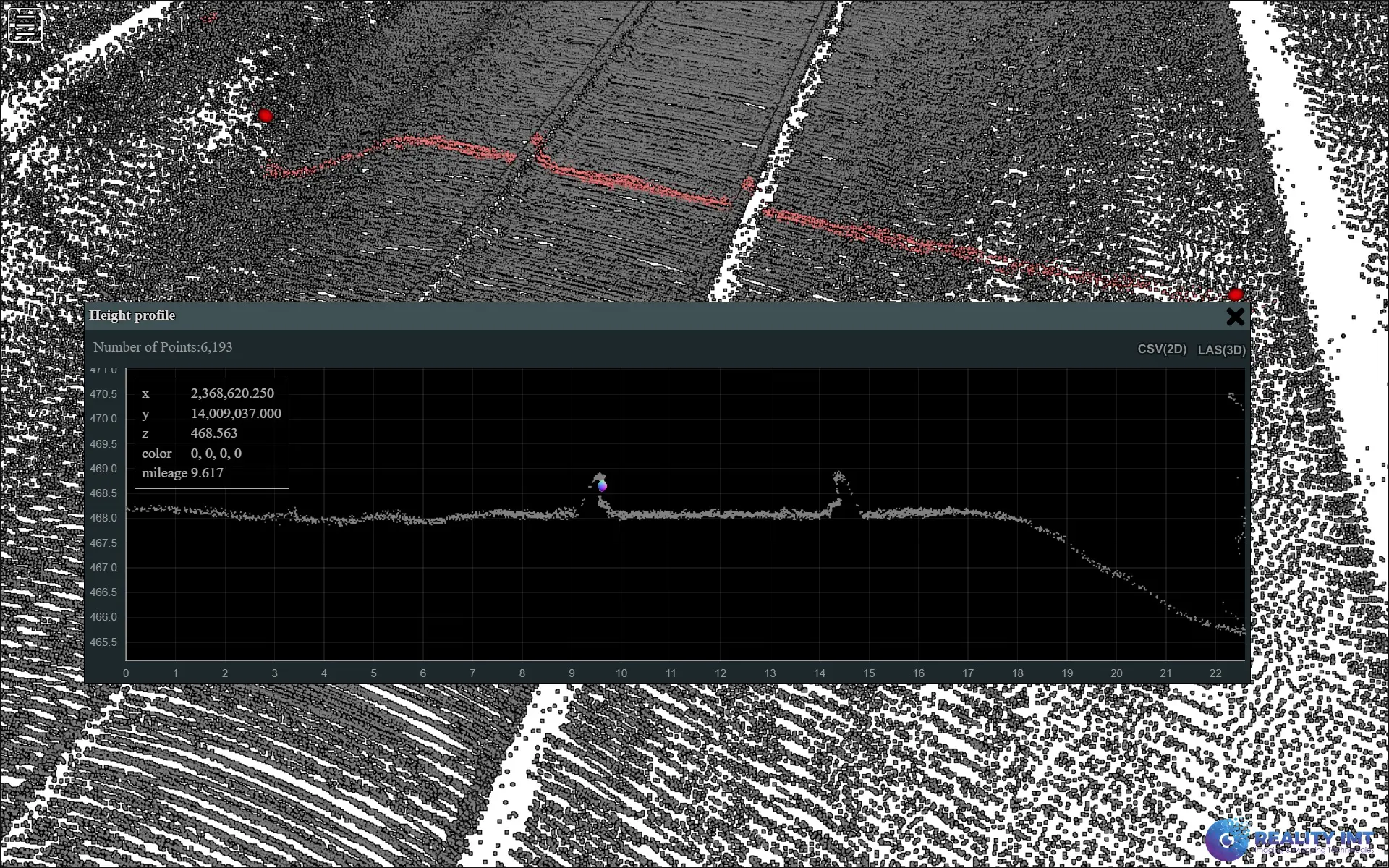
Using cutting-edge technologies like LiDAR and high-definition imagery, the survey team captures detailed information about the rail assets. They meticulously record measurements, dimensions, and positional data, creating a comprehensive digital replica of the infrastructure.
3. Data Analysis and Reporting:
The collected data undergoes thorough analysis to identify any discrepancies and compliance issues. A detailed report is generated, highlighting the findings and recommending necessary remedial actions for safety and maintenance.
4. Integration and Management:
The captured data is integrated into sophisticated software systems and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) platforms, allowing easy management and accessibility of the information. This enables decision-makers to access real-time data and make informed choices about maintenance, upgrades, or future planning.
Conclusion:
Rail as-built surveys are an indispensable tool in the railway industry, providing accurate representation of existing assets, enhancing safety, streamlining operations, and supporting infrastructural planning. By leveraging cutting-edge surveying techniques and technologies, railway companies can optimize their performance, improve passenger experiences, and ensure a sustainable and efficient rail network. Embracing rail as-built surveys is a crucial step towards building a future-proof railway system that meets the demands of the modern world.